Blockchain
Blockchain:
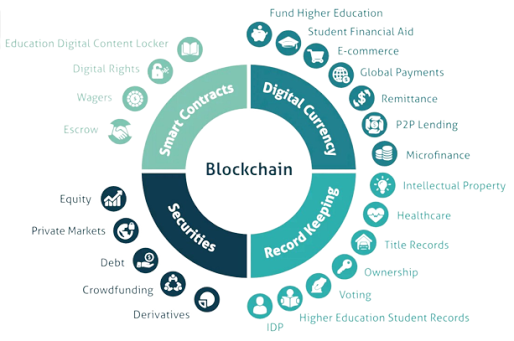.png)
1. A decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers.
2. Each block in the chain contains a record of multiple transactions and is linked to the previous block using cryptography.
3. The decentralized nature of a blockchain makes it secure, as no single entity has control over the data and all participants in the network have a copy of the ledger.
4. This allows for the secure and transparent transfer of digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies, without the need for intermediaries.
5. Blockchains can also be used for non-financial applications, such as supply chain management, voting systems, and record-keeping.
Smart Contract:
- A self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
- The code and the agreements contained within it exist on a blockchain network, allowing for secure and transparent execution without intermediaries.
- Smart contracts can automatically execute when certain predetermined conditions are met, such as the transfer of funds or the fulfillment of obligations.
- This allows for trustless and automated transactions, making the process more efficient and reducing the risk of fraud.
Securities in Blockchain:
- Blockchain technology can be used to issue and trade securities, such as stocks and bonds, in a more efficient and secure manner.
- This can be done through the creation of digital tokens that represent ownership of an asset.
- These tokens can be bought and sold on a blockchain-based platform, allowing for a decentralized and transparent marketplace for securities.
- The use of smart contracts can also automate the settlement and transfer of ownership, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
- Blockchain-based securities have the potential to increase access to capital, particularly for smaller companies and emerging markets, while also reducing the risk of fraud and increasing transparency in the trading process.
Record Keeping in Blockchain:
- Blockchain technology provides a secure and tamper-proof way of keeping records.
- The decentralized ledger of transactions allows for the creation of a single source of truth, accessible by all parties involved.
- This can lead to improved accuracy and efficiency in record-keeping, as well as reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
- Blockchain-based record-keeping can be applied in various industries, such as finance, healthcare, real estate, and voting systems.
It can also be used to verify the authenticity of sensitive information, such as certificates, licenses, and degrees.
Digital Currency in Blockchain:
- Digital currencies, also known as cryptocurrencies, are digital assets that use cryptography and decentralized ledger technology to function as a medium of exchange.
- The most well-known digital currency is Bitcoin, but there are many others, such as Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin.
- Digital currencies can be used to securely transfer value and make payments without the need for intermediaries, such as banks.
- Transactions are recorded on a blockchain ledger and are secured through cryptography, making them secure and transparent.
- Digital currencies also offer increased financial freedom and privacy, as users can make transactions without having to reveal their identities.
- However, digital currencies can also be subject to high volatility, as well as regulatory and security risks.
Blockchain:
.png)
1. A decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers.
2. Each block in the chain contains a record of multiple transactions and is linked to the previous block using cryptography.
3. The decentralized nature of a blockchain makes it secure, as no single entity has control over the data and all participants in the network have a copy of the ledger.
3. The decentralized nature of a blockchain makes it secure, as no single entity has control over the data and all participants in the network have a copy of the ledger.
4. This allows for the secure and transparent transfer of digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies, without the need for intermediaries.
5. Blockchains can also be used for non-financial applications, such as supply chain management, voting systems, and record-keeping.
Smart Contract:
- A self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
- The code and the agreements contained within it exist on a blockchain network, allowing for secure and transparent execution without intermediaries.
- Smart contracts can automatically execute when certain predetermined conditions are met, such as the transfer of funds or the fulfillment of obligations.
- This allows for trustless and automated transactions, making the process more efficient and reducing the risk of fraud.
Securities in Blockchain:
- Blockchain technology can be used to issue and trade securities, such as stocks and bonds, in a more efficient and secure manner.
- This can be done through the creation of digital tokens that represent ownership of an asset.
- These tokens can be bought and sold on a blockchain-based platform, allowing for a decentralized and transparent marketplace for securities.
- The use of smart contracts can also automate the settlement and transfer of ownership, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
- Blockchain-based securities have the potential to increase access to capital, particularly for smaller companies and emerging markets, while also reducing the risk of fraud and increasing transparency in the trading process.
Record Keeping in Blockchain:
- Blockchain technology provides a secure and tamper-proof way of keeping records.
- The decentralized ledger of transactions allows for the creation of a single source of truth, accessible by all parties involved.
- This can lead to improved accuracy and efficiency in record-keeping, as well as reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
- Blockchain-based record-keeping can be applied in various industries, such as finance, healthcare, real estate, and voting systems.
It can also be used to verify the authenticity of sensitive information, such as certificates, licenses, and degrees.
Digital Currency in Blockchain:
- Digital currencies, also known as cryptocurrencies, are digital assets that use cryptography and decentralized ledger technology to function as a medium of exchange.
- The most well-known digital currency is Bitcoin, but there are many others, such as Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin.
- Digital currencies can be used to securely transfer value and make payments without the need for intermediaries, such as banks.
- Transactions are recorded on a blockchain ledger and are secured through cryptography, making them secure and transparent.
- Digital currencies also offer increased financial freedom and privacy, as users can make transactions without having to reveal their identities.
- However, digital currencies can also be subject to high volatility, as well as regulatory and security risks.
Comments
Post a Comment